If equipment regularly breaks down or requires costly repairs, it may be time to consider investing in new equipment. Virtual and augmented reality technologies allow manufacturers to simulate and visualize different scenarios and processes in a virtual environment. This can be particularly useful for training employees, testing new equipment and processes, and identifying potential areas for improvement before implementing them in the real world. Companies need a team or individual responsible for monitoring and analyzing efficiency variance. Here are some people or departments responsible for monitoring and analyzing efficiency variance in a company.
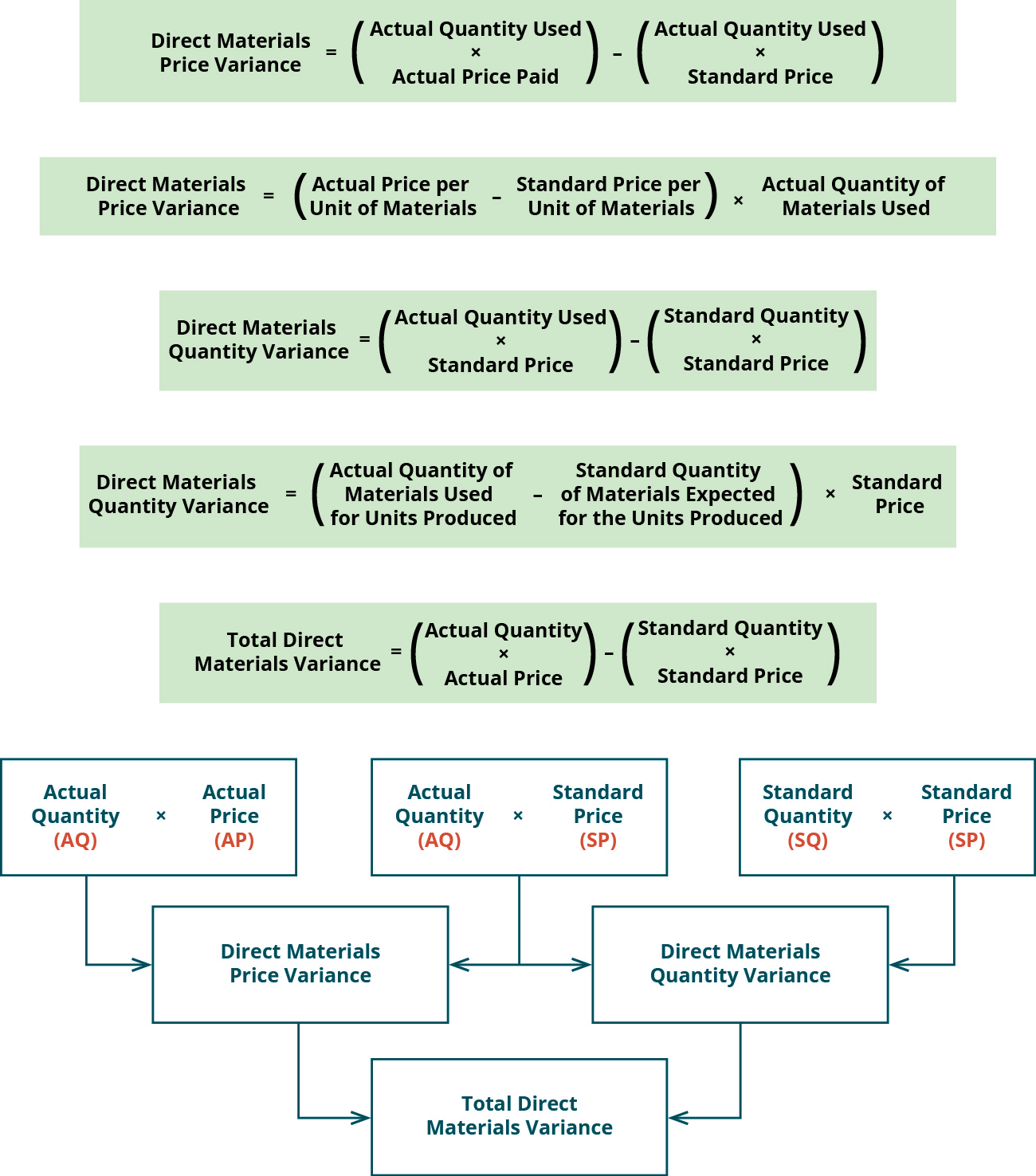
What is the formula for the direct materials price variance?
- Or, further investigation might reveal a production error in which the units were improperly sized, which is a significant quality control issue.
- Our work has been directly cited by organizations including Entrepreneur, Business Insider, Investopedia, Forbes, CNBC, and many others.
- The amounts for each column are computed in the order indicated in the headings.
- At Finance Strategists, we partner with financial experts to ensure the accuracy of our financial content.
- Inaccurate forecasting of demand or production requirements can lead to inefficiencies, such as overproduction, underproduction, or excess inventory.
Standards for variable manufacturing costs include both quantity and price standards. The quantity standard establishes how much of an input is needed to make a product or provide a service. These standards can be used to make financial projections and to evaluate performance by comparing the standards to actual performance at the end of the period. Any discrepancy between the standard and actual costs is known as a variance.
Overhead Variance – Types of Efficiency Variance
As a result of this unfavorable outcome information, the company may consider retraining workers to reduce waste or change their production process to decrease materials needs per box. In this case, the actual quantity of materials used is \(0.50\) pounds, the standard price per unit of materials is \(\$7.00\), and the standard quantity used is \(0.25\) pounds. To illustrate standard costs variance analysis for variable manufacturing overhead, refer to the data for NoTuggins in Exhibit 8-1 above. Per the standards, the variable manufacturing overhead rate is $3 and each unit requires 0.25 direct labor hours. During the period, 45,000 direct labor hours were actually worked and actual variable manufacturing overhead of $121,500 was incurred.
Favorable or unfavorable variance

The standard and actual amounts for direct labor hours, rates, and totals are calculated in the top section of the direct labor variance template. Once the top section is complete, the amounts from the top section can be plugged into the formulas to compute the direct labor efficiency (quantity) and rate (price) variances. The total direct labor variance can be calculated in the last line of the top section by subtracting what is a depreciation tax shield the actual amounts from the standard amounts. The standard quantity allowed of 37,500 direct labor hours less the actual hours worked of 45,000 hours yields a variance of (7,500) direct labor hours. The direct labor rate per hour variance is calculated as the projected standard direct labor rate of $18 per hour, less the actual direct labor rate of $18.50, which yields a $(0.50) unfavorable per hour rate variance.
Age And Condition of Current Equipment – When Should a Company Consider Investing in New Equipment
Examples of indirect labor include wages paid to the production supervisor or quality control team. While they are a part of the production process, it would be difficult to trace these wages to the production of a single desk. Indirect labor is included in the manufacturing overhead category, not the direct labor category. The quality control manager is responsible for ensuring that products meet the quality standards set by the company.
If, however, the actual price paid per unit of material is greater than the standard price per unit, the variance will be unfavorable. An unfavorable outcome means you spent more on the purchase of materials than you anticipated. A template to compute the standard cost variances related to direct material, direct labor, and variable manufacturing overhead is presented in Exhibit 8-11.
How much is the direct materials quantity variance of Prime Furniture Inc. for the month of December 2022? With either of these formulas, the actual quantity used refers to the actual amount of materials used at the actual production output. The standard quantity is the expected amount of materials used at the actual production output. If there is no difference between the actual quantity used and the standard quantity, the outcome will be zero, and no variance exists. To illustrate standard costs variance analysis for direct materials, refer to the data for NoTuggins in Exhibit 8-1 above. The direct material standards for one unit of NoTuggins are 4.2 feet of flat nylon cord that costs $0.50 per foot for a total direct material cost per unit of $2.10.
If the outcome is favorable (a negative outcome occurs in the calculation), this means the company was more efficient than what it had anticipated for variable overhead. If the outcome is unfavorable (a positive outcome occurs in the calculation), this means the company was less efficient than what it had anticipated for variable overhead. Suppose Connie’s Candy budgets capacity of production at 100% and determines expected overhead at this capacity.

